
【校招VIP】SpringBoot启动过程-面试题
 csdn
10月18日
csdn
10月18日

转载声明:文章来源https://blog.csdn.net/jason_jiahongfei/article/details/121842807
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
/**
* Hello world!
*
*/
@SpringBootApplication
public class App
{
public static void main( String[] args )
{
System.out.println( "Hello World!" );
SpringApplication.run(App.class,args);
}
}一、Spring SPI机制,自动装配:
启动类使用@SpringApplication注解,看一下注解代码:
代码中使用@EnableAutoConfiguration以及@ComponentScan自动装配
其中注解@EnableAutoConfiguration使用了@Import加载,最后使用了SpringFactoriesLoader反射出maven中META-INF下spring.factories。
public @interface SpringBootApplication {
@AliasFor(
annotation = EnableAutoConfiguration.class
)
Class<?>[] exclude() default {};
@AliasFor(
annotation = EnableAutoConfiguration.class
)
String[] excludeName() default {};
@AliasFor(
annotation = ComponentScan.class,
attribute = "basePackages"
)
String[] scanBasePackages() default {};
@AliasFor(
annotation = ComponentScan.class,
attribute = "basePackageClasses"
)
Class<?>[] scanBasePackageClasses() default {};
}
package org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure;
import java.lang.annotation.Documented;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Inherited;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Import;
@Target({ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Inherited
@AutoConfigurationPackage
@Import({AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class})
public @interface EnableAutoConfiguration {
String ENABLED_OVERRIDE_PROPERTY = "spring.boot.enableautoconfiguration";
Class<?>[] exclude() default {};
String[] excludeName() default {};
}
//
public class AutoConfigurationImportSelector ...{
...
protected List<String> getCandidateConfigurations(AnnotationMetadata metadata, AnnotationAttributes attributes) {
//加载类路径下面 META-INF/spring.factories
List<String> configurations = SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(this.getSpringFactoriesLoaderFactoryClass(), this.getBeanClassLoader());
Assert.notEmpty(configurations, "No auto configuration classes found in META-INF/spring.factories. If you are using a custom packaging, make sure that file is correct.");
return configurations;
}
}
public abstract class SpringFactoriesLoader {
public static final String FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION = "META-INF/spring.factories";
.....
public static List<String> loadFactoryNames(Class<?> factoryClass, @Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
String factoryClassName = factoryClass.getName();
return (List)loadSpringFactories(classLoader).getOrDefault(factoryClassName, Collections.emptyList());
}
private static Map<String, List<String>> loadSpringFactories(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
MultiValueMap<String, String> result = (MultiValueMap)cache.get(classLoader);
if (result != null) {
return result;
} else {
try {
Enumeration<URL> urls = classLoader != null ? classLoader.getResources("META-INF/spring.factories") : ClassLoader.getSystemResources("META-INF/spring.factories");
LinkedMultiValueMap result = new LinkedMultiValueMap();
while(urls.hasMoreElements()) {
URL url = (URL)urls.nextElement();
UrlResource resource = new UrlResource(url);
Properties properties = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(resource);
Iterator var6 = properties.entrySet().iterator();
while(var6.hasNext()) {
Entry<?, ?> entry = (Entry)var6.next();
List<String> factoryClassNames = Arrays.asList(StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray((String)entry.getValue()));
result.addAll((String)entry.getKey(), factoryClassNames);
}
}
cache.put(classLoader, result);
return result;
} catch (IOException var9) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unable to load factories from location [META-INF/spring.factories]", var9);
}
}
}
....
}二、SpringBoot启动时通过执行main方法中的SpringApplication.run方法去启动,在run方法中调用了SpringApplication的构造方法,在该构造方法中加载了META-INFA\spring.factories文件配置的ApplicationContextInitializer的实现类和
ApplicationListenerr的实现类: 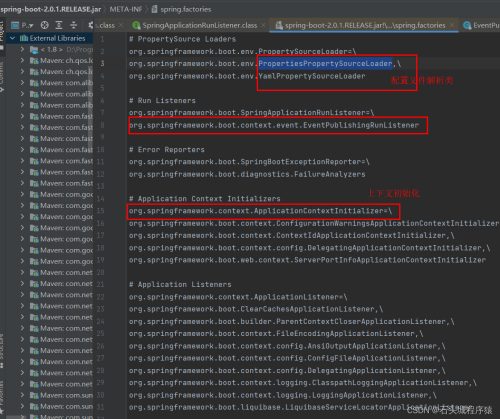
SpringApplication.run(..,..)
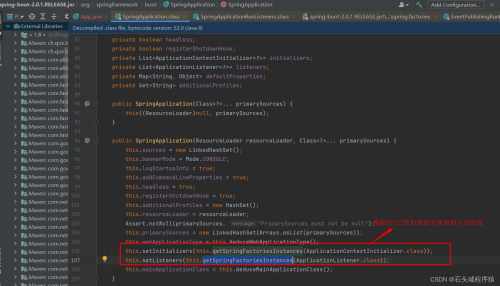
二、ApplicationContextInitializer 这个类当springboot上下文Context初始化完成后会调用。 ApplicationListener当springboot启动时事件change后都会触发。
三、SpringApplication实例构造完之后会调用它的run方法,在run方法中作了以下几步重要操作:
1. 获取事件监听器SpringApplicationRunListener类型,并且执行starting()方法
2. 准备环境,并且把环境跟spring上下文绑定好,并且执行environmentPrepared()方法
3. 创建上下文,根据项目类型创建上下文
4. 执行spring的启动流程扫描并且初始化单实列bean
四、通过@SpringBootApplication注解将ClassPath路径下所有的META-INF\spring.factories文件中的EnableAutoConfiguration实例注入到IOC容器中

沈振衣
01月03日
强~~希望更多人更加努力